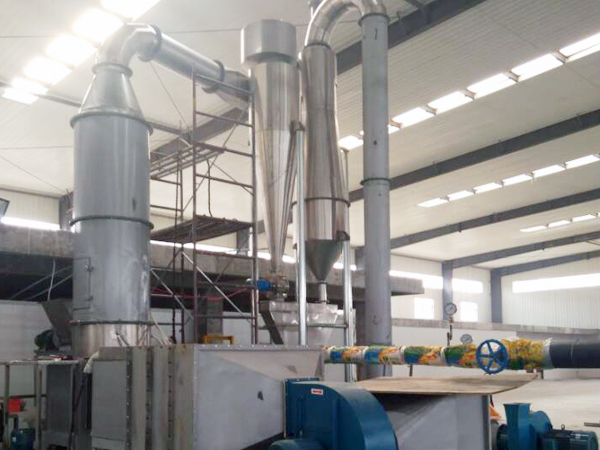
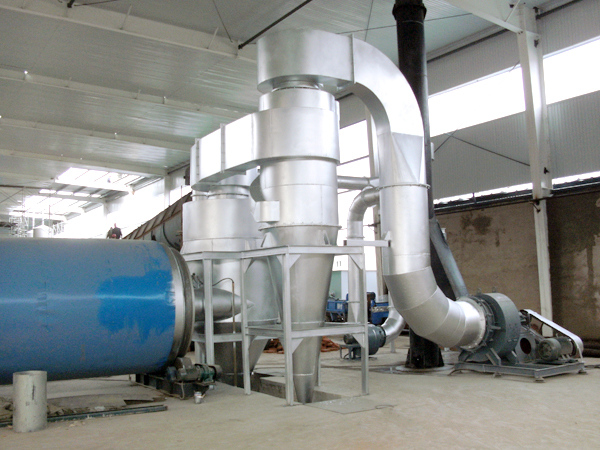
Fluid Bed Dryer Working Principle
Fluid bed dryer is a dryer used for batch or continuous drying of powders, crystals and granulated materials. It can be applied in chemical, pharmaceutical, dairy, foodstuff among other processing industries. Materials drying is achieved through transferring of heat from a fluidizing air stream as it intimately gets into contact with a moist item.
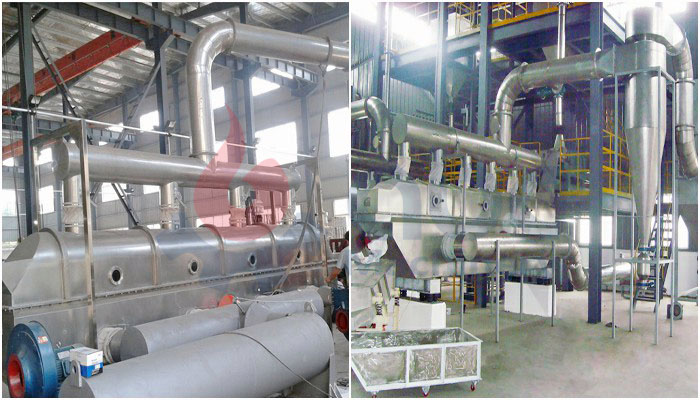

The fluid bed dryer working principle incorporates fluidization of materials
For the drying section, first, the hot air or gas flow is introduced through the bed, which is perforated steel, of solid particles. This is known as the fluidization process. It is achieved when hot air or gas flow is allowed to be in contact with the particle. The hot air or gas will move upwards through the spaces between the particles. The hot air is of sufficient volume lifting the bed of the material thus fluidizes it.
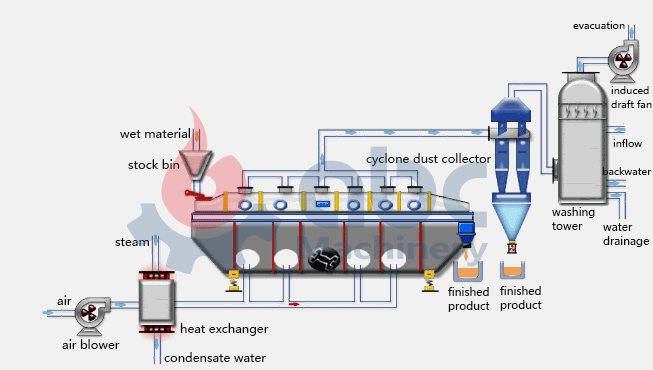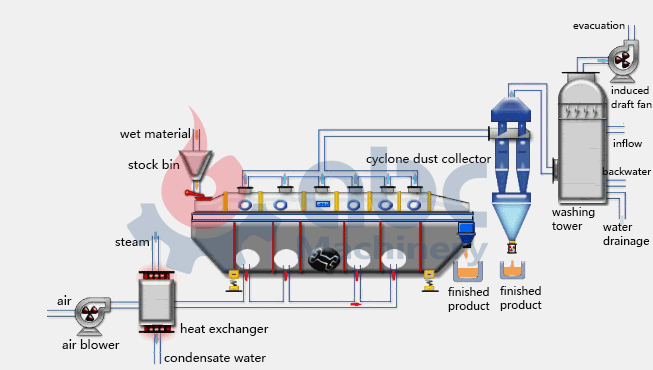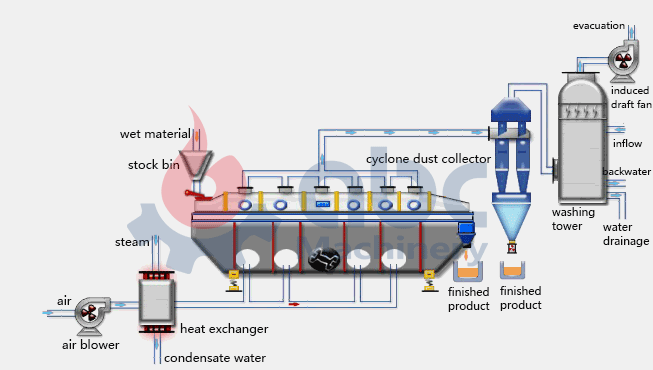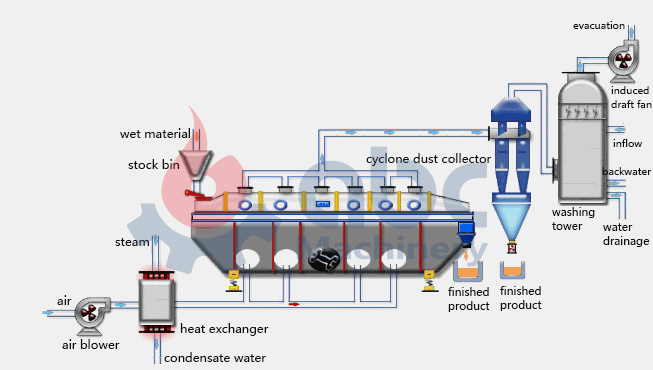
- Upward drag of particles increases with increase in velocity and eventually becomes equal with gravitational forces beneath. Therefore, these particles become suspended in the fluid.
- The shaking of the material moves it along the bed while moisture is transportedby air into the dust recovery system. Here the heated air is then recycled in a closed loop back to the process for further use.
- The temperature and velocity of the air is continuously controlled in order to maximize fluidization as the material is moved the length of the dryer. This enables the wet and sticky materials to be dried effectively.
- The product loses moisture as it passes along the length of the dryer until the targeted dryness is achieved.
High effective drying of particles during fluid bed dryer working process
The inlet air temperature should be appropriately maintained. It should be such that only so much moisture evaporates from the material's surface to avoid formation of surface crusts. This is because the crusts prevents moisture from being carried from deeper layers to the surface thus delaying the entire drying process. In addition, too high air temperature leads to insufficient liquid bridges, inhomogeneous films or instable granulate structures.